Adds an interface to `interp` that can be used to build an interactive debugger, such as those used by IDEs. Closes #1188 All basic debugger features work, with one exception: breakpoints in some locations don't work, due to `setExec` creating a temporary `bltn` (https://github.com/traefik/yaegi/issues/1188#issuecomment-886107905). Example, using a Debug Adapter implementation with VSCode: 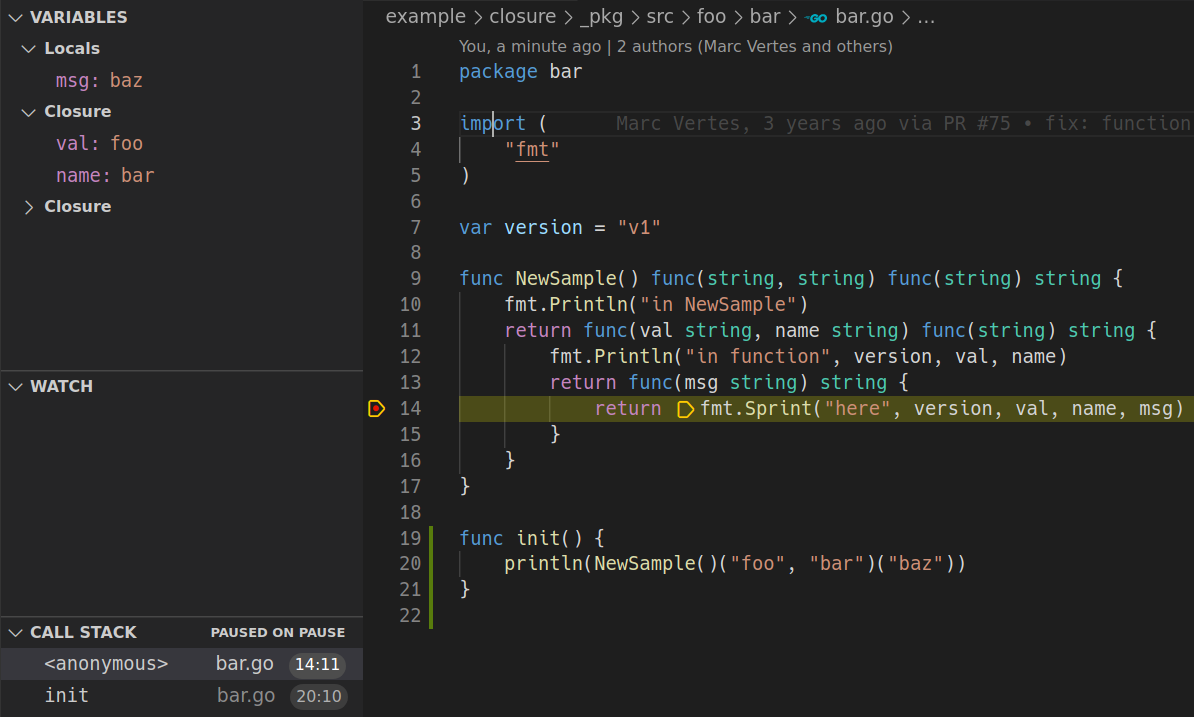
731 lines
17 KiB
Go
731 lines
17 KiB
Go
package interp
|
|
|
|
import (
|
|
"context"
|
|
"errors"
|
|
"fmt"
|
|
"go/token"
|
|
"reflect"
|
|
"sort"
|
|
"sync"
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
var (
|
|
// ErrNotLive indicates that the specified ID does not refer to a (live) Go
|
|
// routine.
|
|
ErrNotLive = errors.New("not live")
|
|
|
|
// ErrRunning indicates that the specified Go routine is running.
|
|
ErrRunning = errors.New("running")
|
|
|
|
// ErrNotRunning indicates that the specified Go routine is running.
|
|
ErrNotRunning = errors.New("not running")
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
var rNodeType = reflect.TypeOf((*node)(nil)).Elem()
|
|
|
|
// A Debugger can be used to debug a Yaegi program.
|
|
type Debugger struct {
|
|
interp *Interpreter
|
|
events func(*DebugEvent)
|
|
context context.Context
|
|
cancel context.CancelFunc
|
|
|
|
gWait *sync.WaitGroup
|
|
gLock *sync.Mutex
|
|
gID int
|
|
gLive map[int]*debugRoutine
|
|
|
|
result reflect.Value
|
|
err error
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// go routine debug state.
|
|
type debugRoutine struct {
|
|
id int
|
|
|
|
mode DebugEventReason
|
|
running bool
|
|
resume chan struct{}
|
|
|
|
fDepth int
|
|
fStep int
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// node debug state.
|
|
type nodeDebugData struct {
|
|
program *Program
|
|
breakOnLine bool
|
|
breakOnCall bool
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// frame debug state.
|
|
type frameDebugData struct {
|
|
g *debugRoutine
|
|
node *node
|
|
name string
|
|
kind frameKind
|
|
scope *scope
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// frame kind.
|
|
type frameKind int
|
|
|
|
const (
|
|
// interpreter root frame.
|
|
frameRoot frameKind = iota + 1
|
|
|
|
// function call frame.
|
|
frameCall
|
|
|
|
// closure capture frame.
|
|
frameClosure
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
// DebugOptions are the debugger options.
|
|
type DebugOptions struct {
|
|
// If true, Go routine IDs start at 1 instead of 0.
|
|
GoRoutineStartAt1 bool
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// A DebugEvent is an event generated by a debugger.
|
|
type DebugEvent struct {
|
|
debugger *Debugger
|
|
reason DebugEventReason
|
|
frame *frame
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// DebugFrame provides access to stack frame information while debugging a
|
|
// program.
|
|
type DebugFrame struct {
|
|
event *DebugEvent
|
|
frames []*frame
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// DebugFrameScope provides access to scoped variables while debugging a
|
|
// program.
|
|
type DebugFrameScope struct {
|
|
frame *frame
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// DebugVariable is the name and value of a variable from a debug session.
|
|
type DebugVariable struct {
|
|
Name string
|
|
Value reflect.Value
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// DebugGoRoutine provides access to information about a Go routine while
|
|
// debugging a program.
|
|
type DebugGoRoutine struct {
|
|
id int
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Breakpoint is the result of attempting to set a breakpoint.
|
|
type Breakpoint struct {
|
|
// Valid indicates whether the breakpoint was successfully set.
|
|
Valid bool
|
|
|
|
// Position indicates the source position of the breakpoint.
|
|
Position token.Position
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// DebugEventReason is the reason a debug event occurred.
|
|
type DebugEventReason int
|
|
|
|
const (
|
|
// continue execution normally.
|
|
debugRun DebugEventReason = iota
|
|
|
|
// DebugPause is emitted when a pause request is completed. Can be used with
|
|
// Interrupt to request a pause.
|
|
DebugPause
|
|
|
|
// DebugBreak is emitted when a debug target hits a breakpoint.
|
|
DebugBreak
|
|
|
|
// DebugEntry is emitted when a debug target starts executing. Can be used
|
|
// with Step to produce a corresponding event when execution starts.
|
|
DebugEntry
|
|
|
|
// DebugStepInto is emitted when a stepInto request is completed. Can be
|
|
// used with Step or Interrupt to request a stepInto.
|
|
DebugStepInto
|
|
|
|
// DebugStepOver is emitted when a stepOver request is completed. Can be
|
|
// used with Step or Interrupt to request a stepOver.
|
|
DebugStepOver
|
|
|
|
// DebugStepOut is emitted when a stepOut request is completed. Can be used
|
|
// with Step or Interrupt to request a stepOut.
|
|
DebugStepOut
|
|
|
|
// DebugTerminate is emitted when a debug target terminates. Can be used
|
|
// with Interrupt to attempt to terminate the program.
|
|
DebugTerminate
|
|
|
|
// DebugEnterGoRoutine is emitted when a Go routine is entered.
|
|
DebugEnterGoRoutine
|
|
|
|
// DebugExitGoRoutine is emitted when a Go routine is exited.
|
|
DebugExitGoRoutine
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
// Debug initializes a debugger for the given program.
|
|
//
|
|
// The program will not start running until Step or Continue has been called. If
|
|
// Step is called with DebugEntry, an entry event will be generated before the
|
|
// first statement is executed. Otherwise, the debugger will behave as usual.
|
|
func (interp *Interpreter) Debug(ctx context.Context, prog *Program, events func(*DebugEvent), opts *DebugOptions) *Debugger {
|
|
dbg := new(Debugger)
|
|
dbg.interp = interp
|
|
dbg.events = events
|
|
dbg.context, dbg.cancel = context.WithCancel(ctx)
|
|
dbg.gWait = new(sync.WaitGroup)
|
|
dbg.gLock = new(sync.Mutex)
|
|
dbg.gLive = make(map[int]*debugRoutine, 1)
|
|
|
|
if opts == nil {
|
|
opts = new(DebugOptions)
|
|
}
|
|
if opts.GoRoutineStartAt1 {
|
|
dbg.gID = 1
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
mainG := dbg.enterGoRoutine()
|
|
mainG.mode = DebugEntry
|
|
|
|
interp.debugger = dbg
|
|
interp.frame.debug = &frameDebugData{kind: frameRoot, g: mainG}
|
|
|
|
prog.root.Walk(func(n *node) bool {
|
|
n.setProgram(prog)
|
|
return true
|
|
}, nil)
|
|
|
|
go func() {
|
|
defer func() { interp.debugger = nil }()
|
|
defer events(&DebugEvent{reason: DebugTerminate})
|
|
defer dbg.cancel()
|
|
|
|
<-mainG.resume
|
|
dbg.events(&DebugEvent{dbg, DebugEnterGoRoutine, interp.frame})
|
|
dbg.result, dbg.err = interp.ExecuteWithContext(ctx, prog)
|
|
dbg.exitGoRoutine(mainG)
|
|
dbg.events(&DebugEvent{dbg, DebugExitGoRoutine, interp.frame})
|
|
dbg.gWait.Wait()
|
|
}()
|
|
|
|
return dbg
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Wait blocks until all Go routines launched by the program have terminated.
|
|
// Wait returns the results of `(*Interpreter).Execute`.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) Wait() (reflect.Value, error) {
|
|
<-dbg.context.Done()
|
|
return dbg.result, dbg.err
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// mark entry into a go routine.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) enterGoRoutine() *debugRoutine {
|
|
g := new(debugRoutine)
|
|
g.resume = make(chan struct{})
|
|
|
|
dbg.gWait.Add(1)
|
|
|
|
dbg.gLock.Lock()
|
|
g.id = dbg.gID
|
|
dbg.gID++
|
|
dbg.gLive[g.id] = g
|
|
dbg.gLock.Unlock()
|
|
|
|
return g
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// mark exit from a go routine.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) exitGoRoutine(g *debugRoutine) {
|
|
dbg.gLock.Lock()
|
|
delete(dbg.gLive, g.id)
|
|
dbg.gLock.Unlock()
|
|
|
|
dbg.gWait.Done()
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// get the state for a given go routine, if it's live.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) getGoRoutine(id int) (*debugRoutine, bool) {
|
|
dbg.gLock.Lock()
|
|
g, ok := dbg.gLive[id]
|
|
dbg.gLock.Unlock()
|
|
return g, ok
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// mark entry into a function call.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) enterCall(nFunc, nCall *node, f *frame) {
|
|
if f.debug != nil {
|
|
f.debug.g.fDepth++
|
|
return
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
f.debug = new(frameDebugData)
|
|
f.debug.g = f.anc.debug.g
|
|
f.debug.scope = nFunc.scope
|
|
|
|
switch nFunc.kind {
|
|
case funcLit:
|
|
f.debug.kind = frameCall
|
|
if nFunc.frame != nil {
|
|
nFunc.frame.debug.kind = frameClosure
|
|
nFunc.frame.debug.node = nFunc
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
case funcDecl:
|
|
f.debug.kind = frameCall
|
|
f.debug.name = nFunc.child[1].ident
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if nCall != nil && nCall.anc.kind == goStmt {
|
|
f.debug.g = dbg.enterGoRoutine()
|
|
dbg.events(&DebugEvent{dbg, DebugEnterGoRoutine, f})
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
f.debug.g.fDepth++
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// mark exit from a function call.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) exitCall(nFunc, nCall *node, f *frame) {
|
|
_ = nFunc // ignore unused, so exitCall can have the same signature as enterCall
|
|
|
|
f.debug.g.fDepth--
|
|
|
|
if nCall != nil && nCall.anc.kind == goStmt {
|
|
dbg.exitGoRoutine(f.debug.g)
|
|
dbg.events(&DebugEvent{dbg, DebugExitGoRoutine, f})
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// called by the interpreter prior to executing the node.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) exec(n *node, f *frame) (stop bool) {
|
|
f.debug.node = n
|
|
|
|
if n != nil && n.pos == token.NoPos {
|
|
return false
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
g := f.debug.g
|
|
defer func() { g.running = true }()
|
|
|
|
e := &DebugEvent{dbg, g.mode, f}
|
|
switch {
|
|
case g.mode == DebugTerminate:
|
|
dbg.cancel()
|
|
return true
|
|
|
|
case n.shouldBreak():
|
|
e.reason = DebugBreak
|
|
|
|
case g.mode == debugRun:
|
|
return false
|
|
|
|
case g.mode == DebugStepOut:
|
|
if g.fDepth >= g.fStep {
|
|
return false
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
case g.mode == DebugStepOver:
|
|
if g.fDepth > g.fStep {
|
|
return false
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
dbg.events(e)
|
|
|
|
g.running = false
|
|
select {
|
|
case <-g.resume:
|
|
return false
|
|
case <-dbg.context.Done():
|
|
return true
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Continue continues execution of the specified Go routine. Continue returns
|
|
// ErrNotLive if there is no Go routine with the corresponding ID, or if it is not
|
|
// live.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) Continue(id int) error {
|
|
g, ok := dbg.getGoRoutine(id)
|
|
if !ok {
|
|
return ErrNotLive
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
g.mode = debugRun
|
|
g.resume <- struct{}{}
|
|
return nil
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// update the exec mode of this routine.
|
|
func (g *debugRoutine) setMode(reason DebugEventReason) {
|
|
if g.mode == DebugTerminate {
|
|
return
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if g.mode == DebugEntry && reason == DebugEntry {
|
|
return
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
switch reason {
|
|
case DebugStepInto, DebugStepOver, DebugStepOut:
|
|
g.mode, g.fStep = reason, g.fDepth
|
|
default:
|
|
g.mode = DebugPause
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Step issues a stepInto, stepOver, or stepOut request to a stopped Go routine.
|
|
// Step returns ErrRunning if the Go routine is running. Step returns ErrNotLive
|
|
// if there is no Go routine with the corresponding ID, or if it is not live.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) Step(id int, reason DebugEventReason) error {
|
|
g, ok := dbg.getGoRoutine(id)
|
|
if !ok {
|
|
return ErrNotLive
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if g.running {
|
|
return ErrRunning
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
g.setMode(reason)
|
|
g.resume <- struct{}{}
|
|
return nil
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Interrupt issues a stepInto, stepOver, or stepOut request to a running Go
|
|
// routine. Interrupt returns ErrRunning if the Go routine is running. Interrupt
|
|
// returns ErrNotLive if there is no Go routine with the corresponding ID, or if
|
|
// it is not live.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) Interrupt(id int, reason DebugEventReason) bool {
|
|
g, ok := dbg.getGoRoutine(id)
|
|
if !ok {
|
|
return false
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
g.setMode(reason)
|
|
return true
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Terminate attempts to terminate the program.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) Terminate() {
|
|
dbg.gLock.Lock()
|
|
g := dbg.gLive
|
|
dbg.gLive = nil
|
|
dbg.gLock.Unlock()
|
|
|
|
for _, g := range g {
|
|
g.mode = DebugTerminate
|
|
close(g.resume)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// BreakpointTarget is the target of a request to set breakpoints.
|
|
type BreakpointTarget func(*Debugger, func(*node))
|
|
|
|
// PathBreakpointTarget is used to set breapoints on compiled code by path. This
|
|
// can be used to set breakpoints on code compiled with EvalPath, or source
|
|
// packages loaded by Yaegi.
|
|
func PathBreakpointTarget(path string) BreakpointTarget {
|
|
return func(dbg *Debugger, cb func(*node)) {
|
|
for _, r := range dbg.interp.roots {
|
|
f := dbg.interp.fset.File(r.pos)
|
|
if f != nil && f.Name() == path {
|
|
cb(r)
|
|
return
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// ProgramBreakpointTarget is used to set breakpoints on a Program.
|
|
func ProgramBreakpointTarget(prog *Program) BreakpointTarget {
|
|
return func(_ *Debugger, cb func(*node)) {
|
|
cb(prog.root)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// AllBreakpointTarget is used to set breakpoints on all compiled code. Do not
|
|
// use with LineBreakpoint.
|
|
func AllBreakpointTarget() BreakpointTarget {
|
|
return func(dbg *Debugger, cb func(*node)) {
|
|
for _, r := range dbg.interp.roots {
|
|
cb(r)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
type breakpointSetup struct {
|
|
roots []*node
|
|
lines map[int]int
|
|
funcs map[string]int
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// BreakpointRequest is a request to set a breakpoint.
|
|
type BreakpointRequest func(*breakpointSetup, int)
|
|
|
|
// LineBreakpoint requests a breakpoint on the given line.
|
|
func LineBreakpoint(line int) BreakpointRequest {
|
|
return func(b *breakpointSetup, i int) {
|
|
b.lines[line] = i
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// FunctionBreakpoint requests a breakpoint on the named function.
|
|
func FunctionBreakpoint(name string) BreakpointRequest {
|
|
return func(b *breakpointSetup, i int) {
|
|
b.funcs[name] = i
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// SetBreakpoints sets breakpoints for the given target. The returned array has
|
|
// an entry for every request, in order. If a given breakpoint request cannot be
|
|
// satisfied, the corresponding entry will be marked invalid. If the target
|
|
// cannot be found, all entries will be marked invalid.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) SetBreakpoints(target BreakpointTarget, requests ...BreakpointRequest) []Breakpoint {
|
|
// start with all breakpoints unverified
|
|
results := make([]Breakpoint, len(requests))
|
|
|
|
// prepare all the requests
|
|
setup := new(breakpointSetup)
|
|
target(dbg, func(root *node) {
|
|
setup.roots = append(setup.roots, root)
|
|
setup.lines = make(map[int]int, len(requests))
|
|
setup.funcs = make(map[string]int, len(requests))
|
|
for i, rq := range requests {
|
|
rq(setup, i)
|
|
}
|
|
})
|
|
|
|
// find breakpoints
|
|
for _, root := range setup.roots {
|
|
root.Walk(func(n *node) bool {
|
|
// function breakpoints
|
|
if len(setup.funcs) > 0 && n.kind == funcDecl {
|
|
// reset stale breakpoints
|
|
n.start.setBreakOnCall(false)
|
|
|
|
if i, ok := setup.funcs[n.child[1].ident]; ok && !results[i].Valid {
|
|
results[i].Valid = true
|
|
results[i].Position = dbg.interp.fset.Position(n.start.pos)
|
|
n.start.setBreakOnCall(true)
|
|
return true
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// line breakpoints
|
|
if len(setup.lines) > 0 && n.pos.IsValid() && n.action != aNop && getExec(n) != nil {
|
|
// reset stale breakpoints
|
|
n.setBreakOnLine(false)
|
|
|
|
pos := dbg.interp.fset.Position(n.pos)
|
|
if i, ok := setup.lines[pos.Line]; ok && !results[i].Valid {
|
|
results[i].Valid = true
|
|
results[i].Position = pos
|
|
n.setBreakOnLine(true)
|
|
return true
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
return true
|
|
}, nil)
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
return results
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// GoRoutines returns an array of live Go routines.
|
|
func (dbg *Debugger) GoRoutines() []*DebugGoRoutine {
|
|
dbg.gLock.Lock()
|
|
r := make([]*DebugGoRoutine, 0, len(dbg.gLive))
|
|
for id := range dbg.gLive {
|
|
r = append(r, &DebugGoRoutine{id})
|
|
}
|
|
dbg.gLock.Unlock()
|
|
sort.Slice(r, func(i, j int) bool { return r[i].id < r[j].id })
|
|
return r
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// ID returns the ID of the Go routine.
|
|
func (r *DebugGoRoutine) ID() int { return r.id }
|
|
|
|
// Name returns "Goroutine {ID}".
|
|
func (r *DebugGoRoutine) Name() string { return fmt.Sprintf("Goroutine %d", r.id) }
|
|
|
|
// GoRoutine returns the ID of the Go routine that generated the event.
|
|
func (evt *DebugEvent) GoRoutine() int {
|
|
if evt.frame.debug == nil {
|
|
return 0
|
|
}
|
|
return evt.frame.debug.g.id
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Reason returns the reason for the event.
|
|
func (evt *DebugEvent) Reason() DebugEventReason {
|
|
return evt.reason
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Walk the stack trace frames. The root frame is included if and only if it is
|
|
// the only frame. Closure frames are rolled up into the following call frame.
|
|
func (evt *DebugEvent) walkFrames(fn func([]*frame) bool) {
|
|
if evt.frame == evt.frame.root {
|
|
fn([]*frame{evt.frame})
|
|
return
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
var g *debugRoutine
|
|
if evt.frame.debug != nil {
|
|
g = evt.frame.debug.g
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
var frames []*frame
|
|
for f := evt.frame; f != nil && f != f.root && (f.debug == nil || f.debug.g == g); f = f.anc {
|
|
if f.debug == nil || f.debug.kind != frameCall {
|
|
frames = append(frames, f)
|
|
continue
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if len(frames) > 0 {
|
|
if !fn(frames) {
|
|
return
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
frames = frames[:0]
|
|
frames = append(frames, f)
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if len(frames) > 0 {
|
|
fn(frames)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// FrameDepth returns the number of call frames in the stack trace.
|
|
func (evt *DebugEvent) FrameDepth() int {
|
|
if evt.frame == evt.frame.root {
|
|
return 1
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
var n int
|
|
evt.walkFrames(func([]*frame) bool { n++; return true })
|
|
return n
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Frames returns the call frames in the range [start, end).
|
|
func (evt *DebugEvent) Frames(start, end int) []*DebugFrame {
|
|
count := end - start
|
|
if count < 0 {
|
|
return nil
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
frames := []*DebugFrame{}
|
|
evt.walkFrames(func(f []*frame) bool {
|
|
df := &DebugFrame{evt, make([]*frame, len(f))}
|
|
copy(df.frames, f)
|
|
frames = append(frames, df)
|
|
return len(frames) < count
|
|
})
|
|
return frames
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Name returns the name of the stack frame. For function calls to named
|
|
// functions, this is the function name.
|
|
func (f *DebugFrame) Name() string {
|
|
d := f.frames[0].debug
|
|
if d == nil {
|
|
return "<unknown>"
|
|
}
|
|
switch d.kind {
|
|
case frameRoot:
|
|
return "<init>"
|
|
case frameClosure:
|
|
return "<closure>"
|
|
case frameCall:
|
|
if d.name == "" {
|
|
return "<anonymous>"
|
|
}
|
|
return d.name
|
|
default:
|
|
return "<unknown>"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Position returns the current position of the frame. This is effectively the
|
|
// program counter/link register. May return `Position{}`.
|
|
func (f *DebugFrame) Position() token.Position {
|
|
d := f.frames[0].debug
|
|
if d == nil || d.node == nil {
|
|
return token.Position{}
|
|
}
|
|
return f.event.debugger.interp.fset.Position(d.node.pos)
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Program returns the program associated with the current position of the
|
|
// frame. May return nil.
|
|
func (f *DebugFrame) Program() *Program {
|
|
d := f.frames[0].debug
|
|
if d == nil || d.node == nil {
|
|
return nil
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
return d.node.debug.program
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Scopes returns the variable scopes of the frame.
|
|
func (f *DebugFrame) Scopes() []*DebugFrameScope {
|
|
s := make([]*DebugFrameScope, len(f.frames))
|
|
for i, f := range f.frames {
|
|
s[i] = &DebugFrameScope{f}
|
|
}
|
|
return s
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// IsClosure returns true if this is the capture scope of a closure.
|
|
func (f *DebugFrameScope) IsClosure() bool {
|
|
return f.frame.debug != nil && f.frame.debug.kind == frameClosure
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Variables returns the names and values of the variables of the scope.
|
|
func (f *DebugFrameScope) Variables() []*DebugVariable {
|
|
d := f.frame.debug
|
|
if d == nil || d.scope == nil {
|
|
return nil
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
index := map[int]string{}
|
|
scanScope(d.scope, index)
|
|
|
|
m := make([]*DebugVariable, 0, len(f.frame.data))
|
|
for i, v := range f.frame.data {
|
|
if typ := v.Type(); typ.AssignableTo(rNodeType) || typ.Kind() == reflect.Ptr && typ.Elem().AssignableTo(rNodeType) {
|
|
continue
|
|
}
|
|
name, ok := index[i]
|
|
if !ok {
|
|
continue
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
m = append(m, &DebugVariable{name, v})
|
|
}
|
|
return m
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
func scanScope(sc *scope, index map[int]string) {
|
|
for name, sym := range sc.sym {
|
|
if _, ok := index[sym.index]; ok {
|
|
continue
|
|
}
|
|
index[sym.index] = name
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
for _, ch := range sc.child {
|
|
if ch.def != sc.def {
|
|
continue
|
|
}
|
|
scanScope(ch, index)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|